|
|
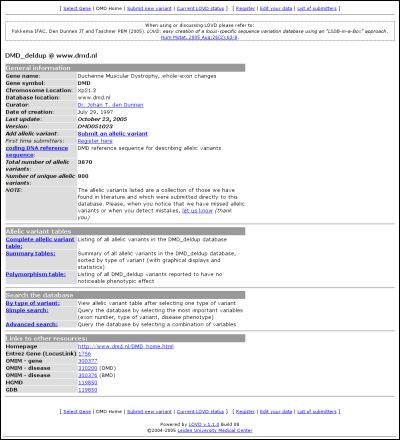
LOVD ManualThe public areaMost of the public area is available without registration. Registration is only necessary for submission of new variants. At the top and the bottom of the screen, a menu is displayed showing your options for the public area.Selecting a geneWhen you have not selected a gene yet, and multiple genes are available in this LOVD installation, this page is the default entry point for the public area. Select the desired gene from the list of available gene databases. Both the gene symbol and the full gene name are provided. After clicking 'Select Database' you are forwarded to the selected gene's homepage.After you have selected a gene, you can always return to this page by clicking on the 'Select Gene' link provided in the menu located both at the top and the bottom of the page. Gene homepage
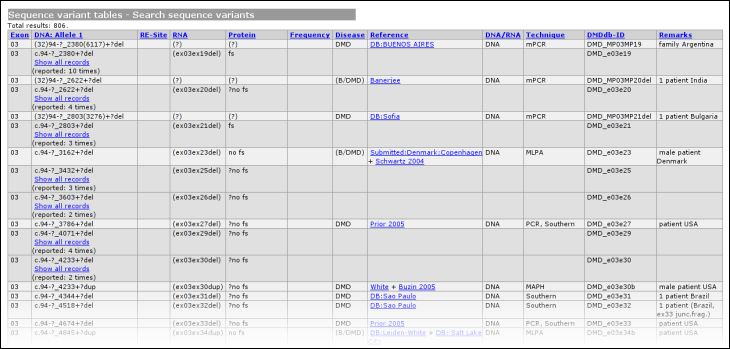
The second table links to the full list of curated allelic variants, the summary (statistics) tables and the polymorphism table. The latter is a full list of curated allelic variants that cause no noticeable effect on the phenotype of the patient. The third table allows you to search the database using three types of searching; by type of variant, simple search, and advanced search. The last table contains links to additional information, configured by the LOVD manager(s). LOVD provides the possibility to easily link to the well-known external data sources Entrez Gene (LocusLink), OMIM, HGMD and GDB. The allelic variantsAll allelic variants displayed are curated by a LOVD manager or curator. Some information contained in the LOVD database is not public as it may harm the privacy of patients.Complete allelic variant tableTo browse the total list of allelic variants in the selected gene database, click on the link "Complete allelic variant table". All curated allelic variants are split into pages of 100 results.Variants that share the same DNA change in both the first and the second allele, are grouped. Also sometimes data is truncated at large lengths. In both cases these entries show up in darker grey compared to the other entries. Grouped records can be viewed as an ungrouped list by clicking on the link 'Show all records'. When information is truncated, the link 'Full details' will show the full listing.
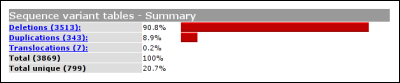
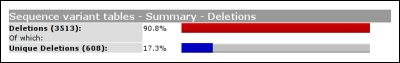
The headers link to the legend, shown at the bottom of the variant list. The legend provides some basic information about what kind of information can be found in what column. From this basic legend, a link is provided to the full LOVD legend. Summary tablesUsing the link 'summary tables' from the gene homepage, some basic statistics about the currently selected gene can be seen.
The second table shows the amount of variants per exon. By default, this table will simply depict how the variants are distributed over the exons. If gene sequence data has been loaded into LOVD, this table will correct for exon length. In this case the percentage of an 100bp exon with 10 variants will equal a 200bp exon with 20 variants.
Polymorphism tableThe polymorphism table is a quick-link to all variants (SNPs) that, according to the reference, do not lead to a change in the phenotype. The format equals that of the complete allelic variant table.Searching specific variants
By type of variantThis form allows you to search by variant type. Dependent on the variants present in the database, you can select substitution, insertion, deletion, duplication, insertion/deletion, inversion or translocation.Simple searchSimple search (see figure) allows you to search the variant list using the exon number, the type of variant and the disease phenotype. All fields are selection lists based on the current contents of the variant list.Advanced searchAdvanced search allows you to search on part of the sequence variation description or the protein change description. Other selection lists that are added compared to the simple search form, are reference, detection template and detection technique.SubmittersFor new data to be added to the system, you must first register with LOVD to be included in the list of submitters. Registration is only necessary for people who wish to submit new variant. Currently it's not possible to keep your name excluded from the list of submitters when registered, but this is planned in a future release of LOVD.Registering a new account
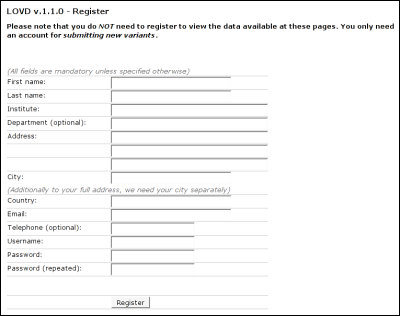
First name: Fill in your first name. Last name: Please fill in your last name. Institute: The (medical) institute you work for. Department: Fill in the department you work for (optional). Address: Use these multiple fields for filling in your full address. City: Repeat your city, which is used to sort your data in the list of submitters and for referring to your institute. Country: Fill in the international name for your country. Email: Fill in your email address. This email address will be used to send copies of submissions to you. Telephone: Fill in your telephone number (optional). Username: Pick a username. It has to be unique; e.g. when you fill in a username that is already taken by another submitter, you will have to pick another one. Password: Fill in your password. Password (repeated): Retype your password. This is to make sure the password is put in the database correctly, it is less likely for you to make a typo twice. Keeping your account up to dateIt is important that you keep your account op to date, as curators or other researchers may want to contact you regarding a variant you submitted.To update your account, click on 'Edit your data' in the LOVD public menu. If you're not currently logged in, you will be asked for your login details. After that, you are provided a form similar to the registration form. Submitting new variantsTo submit a new sequence variant, click on the 'Submit new variant' link in the menu. If you're not currently logged in, you will be asked for your login details. If the LOVD installation has more than one gene, you will see a list of the installed genes for which you can submit a new entry. The currently selected gene will be pre-selected.
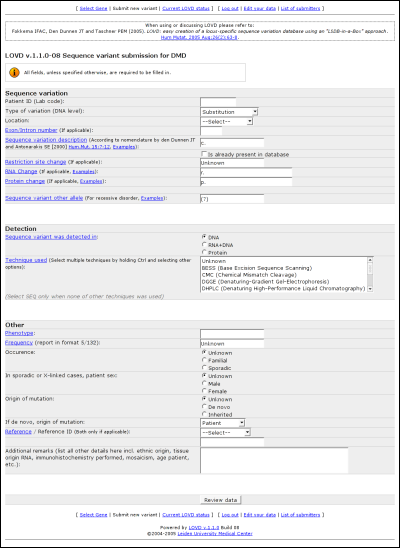
Field names in blue provide links to the full legend with more information on what should go into the field. Sequence variationPatient ID (Lab code):Put in the lab code of the patient, used to describe different patients from the same reference without publishing private information. Type of variation (DNA level): Select one from the following sequence variation types: Substitution, Deletion, Duplication, Insertion, Inversion, Insertion/Deletion, Translocation or Other/Complex. Location: In which region does the variant exist? If it spans more than one region, in which region can the first nucleotide change be found? Choose from 5' Gene flanking, 5' UTR, Exon, Intron, 3' UTR or 3' Gene flanking. Exon/Intron number: In case the variant is found in an exon or an intron, please provide the number. Sequence variation description: Fill in the sequence variant description according to the HGVS recommended nomenclature. Is already present in database: Check this box if the variant has already been described in the database. Restriction site change: Whether or not any restriction site got created or removed because of the variant. RNA Change: Specify the change in mRNA caused by the variant. Protein change: The change on protein, if applicable. When there is no change on protein level, you can leave this field blank or fill in an '='. Sequence variant other allele: If a variant has been detected on the other allele, please provide it here. DetectionSequence variant was detected in:Please select the detection template: DNA, RNA and DNA, or protein. Technique used: Select or fill in the detection technique(s) used to determine the sequence variant. OtherPhenotype:Please select or fill in the phenotype associated with the variant. If no change was detected in the patient's phenotype, fill in 'normal' here. Frequency: Fill in the variant's frequency, in the format: number of variant alleles/number of control alleles tested. Occurrence: The occurrence of the variant, if known. Patient sex: The patient's gender, if known. Origin of mutation: Please select whether the mutation is known to be de novo or whether is has been inherited generation upon generation. If de novo, origin of mutation: If the variant is known to be de novo, select the variant's origin. Reference / Reference ID: If your reference is one out of the standard set of references, select that reference type and fill in the ID in the second field. If your reference if none out of the list, fill in your reference in the second field. If you fill in no reference, you will be listed. Additional remarks: Fill in any remaining information that you may have on the variant, patient or sample(s). LOVD statusA listing of all configured genes with their total amount of entries and their amount of unique entries can be viewed when clicking the 'Current LOVD status' link in the public menu. At the bottom of the page, the total amount of genes, the total amount of variants and the total amount of unique variants are listed. This list is directly taken from the database; the time shown on the top of the page corresponds with the time the figures have been retrieved from the database.
|